Expressvpn Glossary
Identity and access management (IAM)
What is identity and access management?
Identity and access management (IAM) is a framework of policies, processes, and technologies that ensures the right individuals and systems have the appropriate access to organizational resources. It consists of two parts: identity management focuses on confirming who a user or device is, while access management decides what that identity is allowed to do.
How does identity and access management work?
Identity management maintains an up-to-date record of each user or system. It verifies login attempts by checking credentials, such as passwords or multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes, against this identity data.
After authentication succeeds, access management uses the roles or policies associated with that identity to determine which systems, applications, or data can be accessed.
Throughout these steps, the IAM system logs authentication and authorization events to support auditing, compliance, and threat detection.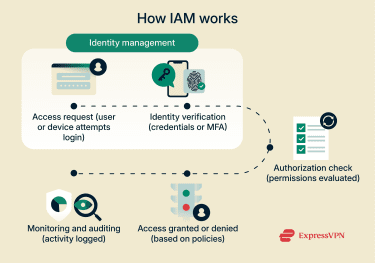
Key components of access management
Access management brings several tools together to manage rights and controls. These include:
- Single sign-on (SSO): Allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without having to log in repeatedly.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Requires two or more verification methods to strengthen identity checks.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Assigns permissions based on job role or group membership.
- Policy enforcement point (PEP): Applies access rules and ensures that every request complies with policy.
- Access logs: Record authentication events and access activity for monitoring and compliance.
Why is identity and access management important?
IAM is important because it ensures that only verified and authorized users can access an organization’s systems and data. It also simplifies account administration by centralizing identity records and access controls, which improves consistency and reduces operational errors.
IAM protects sensitive information through controlled permissions, supports compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001, and aligns with zero-trust security models by validating identity and permissions for each request.
Security and privacy considerations
Strong identity and access management work best when paired with other security measures. These include:
- Managing the identity lifecycle: Maintains accurate identity records and associated access as roles change.
- Using directory services: Centralizes identity data to provide a consistent source for authentication and authorization.
- Using federated identity: Allows identities to be used across different systems or organizations without separate accounts.
- Adding virtual private network (VPN) encryption: A corporate VPN can protect remote and mobile connections by encrypting traffic before it reaches protected resources.
Common identity and access management tools
- Okta: Provides cloud-based access controls with centralized authentication, role-based permissions, and policy enforcement.
- Microsoft Entra ID: Manages access across Microsoft 365, cloud platforms, and on-premises systems using unified policies and conditional access.
- Ping Identity: Delivers access control for large or distributed environments with identity federation and fine-grained authorization.
- IBM Security Verify: Applies access policies across enterprise systems and tracks resource usage to support monitoring and compliance.
Further reading
- Identity theft prevention: How to protect your personal and financial information
- What can someone do with your ID?
- What is data encryption?
FAQ
What’s the difference between IAM and PAM?
Identity and access management (IAM) manages identities and their access across an organization, covering all users and systems. Privileged access management (PAM) focuses specifically on privileged accounts that have elevated permissions, adding stricter controls to reduce the risk associated with high-level access.
Is identity and access management (IAM) the same as access control?
No. IAM includes identity management, authentication, and authorization. Access control is one part of IAM and refers specifically to enforcing permissions that determine what an authenticated identity can use or do.
How does IAM relate to zero-trust security?
Zero trust relies on continuous verification and least-privilege access. Identity and access management (IAM) provides the identity data, authentication methods, and permission models that zero trust uses to validate each request and limit access to only what is necessary.
Can IAM help prevent data breaches?
Yes. Identity and access management (IAM) reduces the risk of unauthorized access by verifying identities, enforcing appropriate permissions, and removing access when it is no longer needed. Logging and monitoring also help detect suspicious activity early.
