What is the Signal app and how does it keep your messages private?

Signal is a messaging app that’s known for its privacy, but what does it actually offer? This guide covers everything you need to know about Signal and its core features. We took a deep dive into how it protects chats and calls and compared it against similar platforms. In addition, we cover what data Signal collects and take a look at common misconceptions regarding the platform.
What is Signal?
Signal is a free, cross-platform messaging app that’s available on Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux. To register, you’ll need to install it on your phone and sign up with a valid phone number. You can then use Signal’s desktop versions in addition to the mobile apps.
Signal functions much like other popular chat apps. It supports:
- Private text, voice, and video communication
- Group chats
- Secure media and file sharing
- Stories (status updates)
- Location sharing
One of Signal’s defining characteristics is its strong emphasis on user privacy and security.
Who created Signal, and why does it matter?
Signal was created by Moxie Marlinspike, a cryptographer known for developing the Signal Protocol, which protects messages in Signal and other popular apps, such as WhatsApp and Google Messages. Before Signal, he founded Whisper Systems, published research on SSL vulnerabilities, and served as head of security at X (formerly Twitter) after the company acquired Whisper Systems.
Brian Acton, the co-founder of WhatsApp, joined him after leaving Facebook following disagreements over how WhatsApp should be monetized. Acton invested $50 million to help launch the Signal Foundation (the organization behind the Signal messenger app), which runs as a non-profit funded primarily by donations.
No ads, no trackers: Business model breakdown
Signal’s non-profit model is designed to reduce reliance on ad revenue, tracking, and data monetization. As a result, the service does not have the same commercial incentives to collect extensive user information, aligning with its stated focus on user privacy.
Is Signal safe?
Signal is generally viewed as a privacy-focused messaging app because it uses a secure encryption protocol, offers several privacy features to protect everyday conversations, and is designed to collect limited user data.
 Its codebase and encryption protocol are also open source, allowing anyone to review how the system works. This transparency helps highlight issues sooner, supports clearer validation of fixes, and offers a more informed view of Signal’s security and privacy protections.
Its codebase and encryption protocol are also open source, allowing anyone to review how the system works. This transparency helps highlight issues sooner, supports clearer validation of fixes, and offers a more informed view of Signal’s security and privacy protections.
How Signal encrypts your messages and calls
Signal uses end-to-end encryption (E2EE) powered by the open-source Signal protocol. Every message, call, attachment, and group conversation is encrypted in such a way that only the sender and intended recipients can access the content. The app also end-to-end encrypts profile information, which includes your name and photo.
Key features of the Signal protocol include:
- Forward secrecy: Messages are encrypted using regularly updated encryption keys, so one compromised key doesn’t expose past messages.
- Post-quantum protection: Signal has added post-quantum cryptographic protections to the Signal Protocol to help defend against future quantum computing attacks.
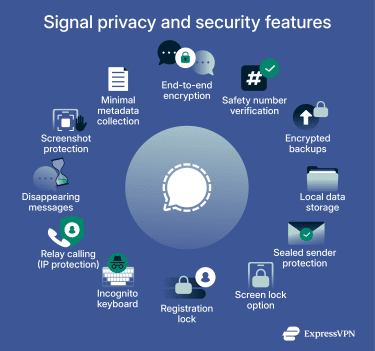
Privacy features for chats and calls
Signal provides a suite of built-in features beyond encryption to keep your conversations private:
Safety number verification
Each user in a one-to-one chat has a unique safety number. The two users can compare their safety numbers either by scanning each other’s QR codes or by sharing the numbers through other means (such as a screenshot or by copy-and-paste). If the numbers match, they can be confident they’re talking to the right person. If they’re different, then it may indicate a potential man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack.
Signal also lets you know if it detects a user’s safety number has changed. Any undelivered messages sent before the change will not be delivered afterward.
However, note that a difference in safety numbers isn’t always indicative of an attack. Moving to another device or reinstalling the Signal app can cause a user to receive a new safety number. If you receive a warning but can otherwise verify that you’re still speaking to the same user, you can manually approve the new safety number.
Secure backups
Signal has a secure backup option that’s end-to-end encrypted. When enabled, it automatically backs up all text messages and the last 45 days of media, including files, photos, and attachments. For a small monthly fee, you can also opt to store up to 100GB of media beyond the 45-day limit. Backups are protected by a unique recovery key that is never shared with the Signal service and is required to restore the data.
Note that disappearing messages and view-once media that are scheduled to disappear within the next 24 hours are excluded from these backups.
Local data storage
Messages, pictures, files, and other media are stored locally on your device by default, not on Signal’s servers. Even if you enable backups, they are encrypted and protected separately. This ensures your chat history isn’t exposed in a server data breach.
Sealed sender protection
Signal also uses a Sealed sender system that limits the amount of sender information the server can access during message delivery. This reduces the amount of metadata Signal can view regarding your conversations. In addition to this, Signal doesn’t store metadata regarding group membership, group titles, group avatars, or group attributes.
Authentication measures
Signal offers a screen lock feature on Android and iOS which prevents the app from being opened without your phone’s PIN, password, or biometric authentication.
It also provides a registration lock. When enabled, this feature requires a user-created Signal PIN to be able to re-register Signal with your phone number. If the PIN cannot be provided, registration must wait out a 7-day inactivity timer, after which a new PIN can be created.
This can prevent attackers who’ve gained physical access to your phone or performed a SIM swap attack from immediately being able to re-register your Signal account and impersonate you (as their messages would be coming from your phone number). You can use the 7-day window to secure your number and notify contacts if needed.
Incognito keyboard
On some Android devices, you can enable the incognito keyboard. This limits how much information your Android keyboards or Input Method Editors (IME) can collect when you use Signal (an IME is a specialized user interface for text input; for example, an interface that converts handwriting into text). This may prevent your typed data from influencing future autocorrections and suggestions. Note that certain keyboards and IMEs can ignore these settings, so it’s important to only use those that you trust.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) vs. relay calling
As mentioned above, audio and video calls on Signal are encrypted. However, Signal uses P2P connections for calls you initiate and those that you receive from your contacts by default, which means your devices directly connect to one another. This can reduce latency and improve call quality, but it also means each caller can potentially see the other’s IP address.
Calls from unknown users are automatically routed through Signal’s servers, which prevents your IP address from being shared. To avoid sharing your IP address with your contacts, you have two options, which we cover below.
Note: The examples in this article use Android, but the steps are generally similar on other devices. Any important differences will be highlighted.
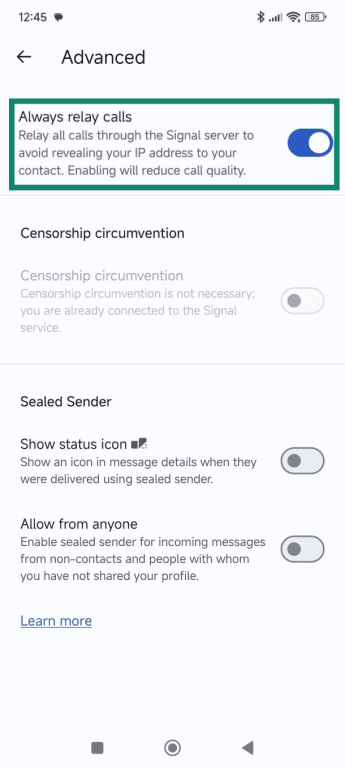
Enable “Aways relay calls”
This option routes all calls through Signal’s servers. Here’s how to turn it on:
- Tap or click the three dots and select Settings. Note that on iOS, you’ll instead need to tap on your avatar, then select Settings.
- Select Privacy.
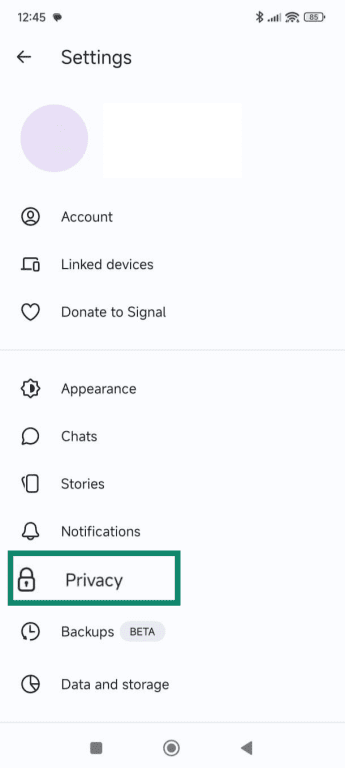
- Scroll down and select Advanced.
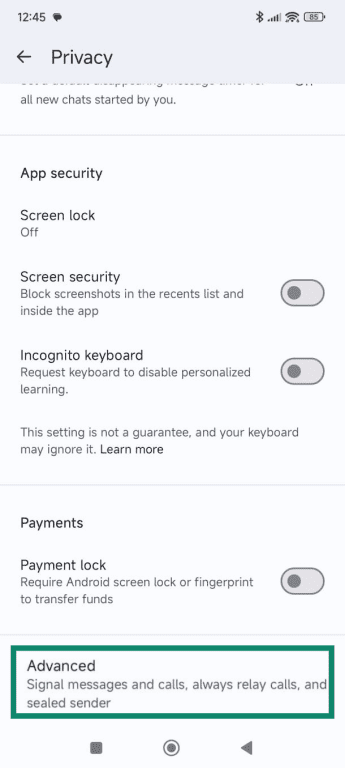
- Toggle on Always relay calls.
Use a secure VPN
If you prefer the performance of P2P calls, but you’d still like to keep your IP address private, you may want to consider a fast and lightweight virtual private network (VPN). A VPN masks your IP address by routing your internet traffic through a secure server; this means the user you’re speaking with can only see the VPN server’s IP, instead of your own.
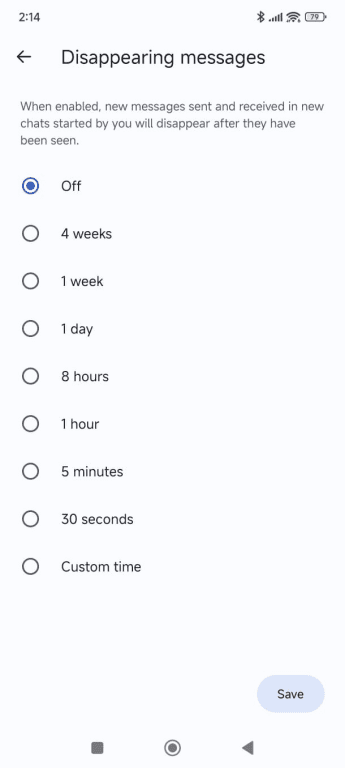
Disappearing messages and view-once media
Chats can be set to disappear after a certain amount of time has passed. Signal allows you to set how long messages remain visible, and you can enable disappearing messages across all chats or choose to only apply the feature to specific conversations.
The timer works differently based on whether you sent or received the disappearing message:
- Sent messages: Timer starts after the message is sent.
- Received messages: Timer starts after you’ve read the message.
For photos and videos, there is also a view-once option. This removes the media from the chat after it’s been viewed.
It’s important to know that these features stop messages and media from being saved in chat histories, but they don’t prevent someone from saving the content in other ways before it disappears, such as via screenshots.
Note: Signal also includes a Screen Security option on Windows 11 to prevent Microsoft Recall from capturing your chat contents. It’s enabled by default and blocks screenshot attempts within Signal Desktop on Windows 11, but it doesn’t stop others from capturing your sent messages or media on their device.
Screen Security can also be enabled on Android and iOS, but it works differently; instead, it prevents Signal previews from appearing on your device’s app switcher, as these could potentially reveal chat contents to users borrowing your device.
How to enable disappearing messages for all your chats
- Tap or click the three dots followed by Settings. If you’re using an iPhone, you’ll instead need to select your avatar, then press Settings.
- Select Privacy.
- Select Disappearing messages.
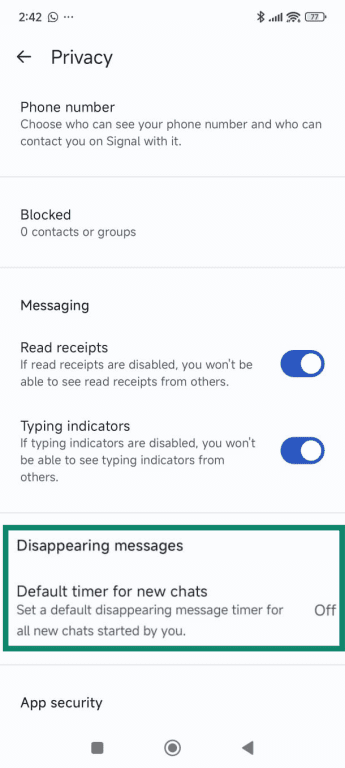
- Pick a time from the list or add a custom time, then tap Save.
How to enable disappearing messages for specific contacts
- Open the chat thread with the relevant contact. Then tap or click the three dots, followed by Chat settings. If you’re on iOS, you’ll instead need to select the contact name, then Chat settings.
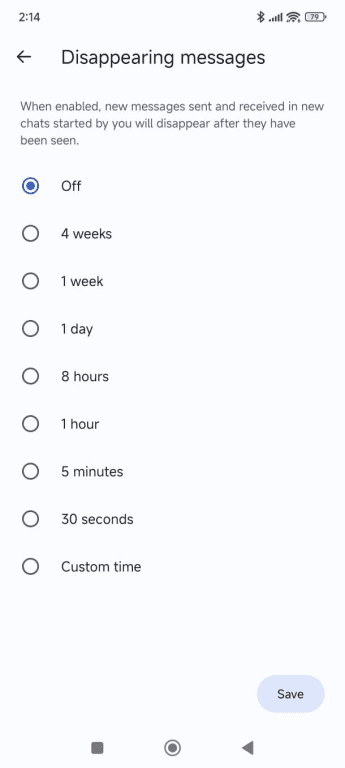
- Select Disappearing messages.
- Pick a time from the list or add a custom time, then hit Save.
How to send view-once photos and videos
- Click the + icon and add a photo or video.
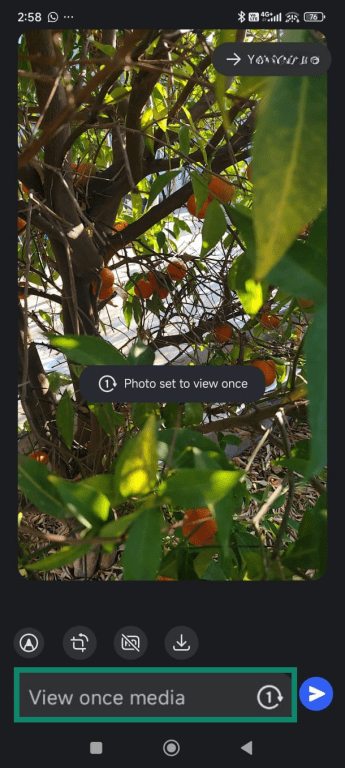
- Tap the infinity icon at the end of the message field.

- The bar will now say “View once media” and the icon will change to a 1. You can now send the media; it can only be viewed once before disappearing.
Data collection and privacy
As we previously covered, Signal limits data collection. However, it does require your phone number to function, though it isn’t shared with other users you chat with by default (excluding those who already have your number saved in their device’s address book). You can also create a username, which allows you to connect to other users without having to share your phone number. You can set your account to not be discoverable through your number, too; users would only be able to find you or start a conversation by entering your exact username.
Signal states in its privacy policy that in addition to your phone number, it only collects the technical information required to provide its services. It can also optionally discover which of your contacts are Signal users, but it protects their privacy via cryptographic hashing. The service doesn’t store message content, contact lists, or details about who you communicate with.
This policy has come to the forefront in past legal requests. When U.S. authorities subpoenaed Signal for user data, the company could only provide the creation date and most recent connection time of the relevant accounts.
Signal vs. WhatsApp vs. Telegram
All three apps have similar features. However, each one approaches privacy, data handling, and monetization differently. Let’s take a closer look at how WhatsApp and Telegram compare to Signal:
| Signal | Telegram | ||
| E2EE | Default for all messages and calls | Default for all messages and calls | Only with the optional secret chats feature |
| Types of data collected | Limited chat and technical metadata; contact data can also be collected, but this is optional | Limited chat metadata, phone number, technical usage data (such as device information), and contact information shared by other users | Chat data from regular cloud chats (not from secret chats), phone number, contacts (if synced), and device and IP information |
| Backups | Opt-in end-to-end encrypted secure backups for the last 45 days of media; optional premium upgrade | Optional cloud backups; encryption depends on settings | Cloud-based based backups |
| Account registration | Phone number required | Phone number required | Phone number required |
| Advertising | No ads | No ads | Only in public broadcast channels |
Common misconceptions and clarifications
There are misconceptions about Signal that circulate online. Some of them are based on outdated information, while others are due to misunderstandings of the relevant technology. Here are a few of the most common:
- Signal can read my messages: This isn't true. E2EE secures Signal messages and calls, meaning only senders and receivers can read them.
- Using a phone number means Signal knows who I contact: Your phone number is used for account registration, but Signal doesn't store your contact list or messaging history on its servers; this data is stored locally. In addition, Signal uses Sealed sender to avoid identifying the sender of any particular message.
- Signal hides everything about my activity: It limits data collection and end-to-end encrypts your communication. However, some technical data, such as your account creation date and last connection time, is still collected by the platform.
- Open-source apps like Signal are less secure because anyone can inspect the code: Open-source design allows independent review and verification. It doesn't weaken the encryption or privacy features. In actuality, this transparency helps identify and fix issues earlier.
FAQ: Common questions about Signal
Why would someone use the Signal app?
Signal is typically used by those who value private communication. It encrypts all messages and calls, doesn't track usage (beyond the time you last used the service), and stores data locally.
Can I use Signal without sharing my phone number?
Signal lets you set a username, allowing you to connect with others without sharing your phone number. You can control how visible your phone number is in Signal’s privacy settings. However, sharing your phone number with Signal is still required to use its services.
How does Signal keep group chats private?
Group data and memberships aren’t stored on Signal’s servers. In addition, all group chats are end-to-end encrypted.
Is Signal really anonymous?
Signal provides numerous features designed to protect privacy, but it’s not fully anonymous. The service needs a phone number to create an account, and limited technical data is also collected by Signal to provide its service.
Can Signal be used safely on desktop?
Yes. The desktop app uses the same encryption and privacy standards.
What should I do if Signal is not working correctly?
You can check your internet connection, update the app, restart it, or reinstall it if needed. Signal’s support pages also include troubleshooting guidance. If you cannot fix the issue, you may want to consider contacting Signal support.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN