DeepSeek vs. ChatGPT: Which AI tool protects your data better?

Large language models (LLMs) have become a part of everyday life for millions of people. Tools like ChatGPT and DeepSeek now handle everything from casual questions to business research and internal workflows.
But when you share information with an AI chatbot, what actually happens to that data?
We took a close look at the privacy policies and terms of use behind ChatGPT and DeepSeek to understand how each platform collects, stores, and uses your data, and what that means for privacy and security in real-world use.
Why security and privacy matter when choosing an AI tool
Data privacy is a key consideration when choosing an AI tool because user input may be logged, retained, or used for training and quality assurance under certain conditions. Prompts are processed on infrastructure operated by the provider, outside the user’s direct control, and are subject to the platform’s data handling policies.
The risk increases as AI becomes embedded in everyday workflows. People use AI chatbots in both personal contexts such as budgeting advice, career decisions, and medical questions, and professional ones such as internal documentation, code review, strategic planning, and more. This is sensitive data that you may not want AI companies using to train their models.
When doing an AI chatbot comparison, security and privacy are just as important as the quality or speed of the responses. Exact data handling practices vary by provider, plan type, and user settings, including whether prompts are retained, reviewed, or used for model improvement. Some questions you should ask yourself are:
- Who can access your data?
- Under what conditions can it be reused?
- How much visibility do you have into what happens after a prompt is submitted?
How DeepSeek and ChatGPT handle user data
When you interact with ChatGPT or DeepSeek, your data moves through several stages after submission. How each platform handles that data is determined by its privacy policy and terms of use.
In practical terms, data handling covers three things:
- How prompts are processed and logged.
- Whether user input can be used beyond the immediate response.
- How long information remains within the provider’s systems.
Data collection and prompt logging
ChatGPT and DeepSeek collect user data as part of operating their services. This includes information you provide, data generated through interaction with the platform, and technical data collected automatically in the background.
DeepSeek
DeepSeek collects personal data when you create an account, submit prompts, upload files, or otherwise interact with the service. This includes account details such as email address, username, and password, as well as conversation content such as prompts, chat history, feedback, and uploaded materials.
It also collects device and network information, such as IP address, device identifiers, operating system, system language, performance logs, and crash reports. DeepSeek assigns device and user IDs to track activity across sessions and devices for security and operational purposes. The company also logs how users interact with features, records approximate location based on IP address for security reasons, and uses cookies and similar technologies to operate and analyze the service.
DeepSeek’s privacy policy also notes that it may receive personal data from third parties, such as login providers, security partners, and publicly available online sources. DeepSeek states that the service is not designed to process sensitive personal data, and it explicitly warns users not to submit such information.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT collects personal data when you create an account, submit prompts, upload content, or communicate with OpenAI. This includes account information such as name, contact details, credentials, and payment information where applicable. User content includes prompts, uploaded files, images, and audio, depending on the features used.
OpenAI also states in its privacy policy that it collects technical data generated through use of the service, like IP address, browser type, timestamps, interaction logs, usage patterns, device information, and general location inferred from IP address. These data points support service functionality, security monitoring, and performance optimization. Cookies and similar technologies are used to maintain preferences and improve the user experience.
In addition, OpenAI receives data from trusted partners, such as security providers and marketing vendors, and states that it collects publicly available information from the internet to develop the models that power its services.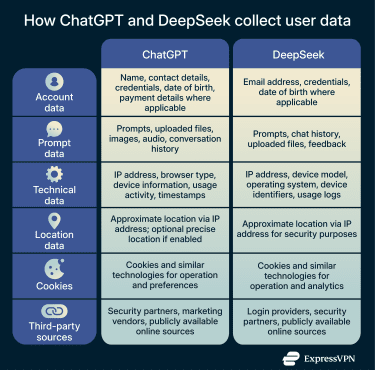
Use of user data for model training
User prompts don’t just generate responses; in some deployments, they may also be collected and analyzed to inform future model improvements.
ChatGPT may apply automated analysis and human review for quality and safety purposes. However, you can change the default data controls in Settings > Data Controls and disable the Improve the model for everyone option, which prevents ChatGPT from using your data for training purposes. When this setting is disabled, future prompts are excluded from training workflows, though previously collected data may still be retained and the content of your chats accessed for other purposes, such as investigating a security incident.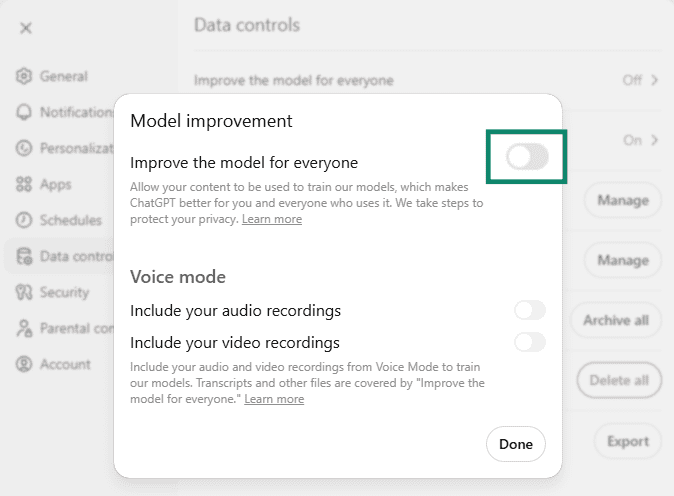
DeepSeek, too, processes user data to operate and improve its services, which can include model development. As with ChatGPT, you can choose not to share your content for training purposes by opening the Settings and turning off the Improve the model for everyone option in the Data section.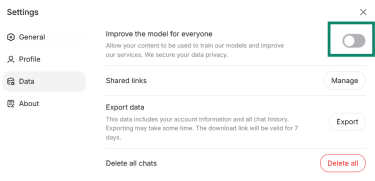
Data retention and deletion controls
Both DeepSeek and ChatGPT retain personal data for operational, legal, and security reasons, but the scope and controls differ in practice.
DeepSeek
DeepSeek keeps personal information for as long as it needs to in order to provide its services and meet legal, business, and contractual obligations. It typically retains account information, user inputs, and payment data for the duration of an active account. If you violate the platform policies, DeepSeek can keep the relevant data even after your account is shut down to investigate or address the violation.
You can delete your chat history through your account settings, although DeepSeek doesn’t say in its privacy policy how long it will take before that data is removed from its servers. There’s also the option to send a request to privacy@deepseek.com and ask that your data be deleted. Some information may still be retained where required for legal or compliance purposes.
ChatGPT
Like DeepSeek, ChatGPT retains personal data for as long as necessary to operate its services or for legitimate business purposes such as security, dispute resolution, and legal compliance. Retention duration depends on factors including the purpose of processing, the sensitivity of the data, potential risk from unauthorized access, and applicable legal obligations.
User settings can influence retention in some cases. For example, temporary chats don’t appear in chat history, but they’re stored on the ChatGPT servers for up to 30 days. The same applies to regular chats that you have deleted from your chat history.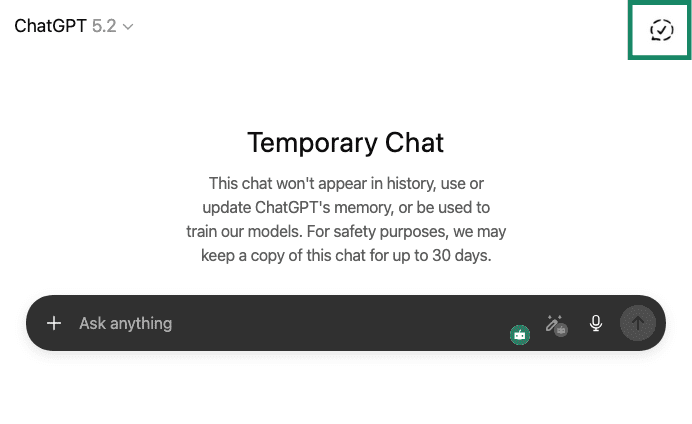
Managing data via ChatGPT’s Privacy Portal
You can access ChatGPT’s Privacy Portal at privacy.openai.com. This is where you can submit formal requests related to your personal data, including deletion, access, correction, and other privacy rights. It goes beyond in-app controls like clearing chat history and lets you make consumer privacy requests direct to OpenAI.
In the Privacy Portal, you can:
- Delete your account and associated personal data: Submitting a “delete my ChatGPT account” request will permanently remove your account and queue data for deletion from OpenAI’s systems, typically within about 30 days.
- Request access or correction: Users with the relevant statutory rights (for example, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU) can ask for access to or correction of their personal information.
- Request removal of personal data from ChatGPT responses: If a ChatGPT response includes identifiable personal information about you (such as your name combined with sensitive or private details), you can submit a removal request. OpenAI will review the request and, if approved, take steps to prevent that specific personal information from being generated in future responses. Note that this option exists as a privacy safeguard and does not mean ChatGPT maintains personal profiles or remembers individual users across conversations.
Overall, the Privacy Portal provides the formal mechanism to exercise your full data rights when the in-app settings aren’t enough.
Open source vs. commercial AI: Privacy by design in practice
AI systems differ in how they’re built, deployed, and governed. One of the most important distinctions is between open-source models, where parts of the system are publicly accessible, and commercial AI services, where the model and infrastructure are centrally controlled by a single provider.
What “open source” means for DeepSeek’s security
In the context of AI, open source refers to making the code available to the public. This allows independent inspection for security issues or unintended behavior in the code itself, particularly in self-hosted deployments.
The DeepSeek model R1 is available on GitHub with an MIT license. This gives free unrestricted use, modification, and distribution, including for commercial purposes, to anyone.
From a security and privacy standpoint, the license has several implications:
- The model can be self-hosted, keeping prompts and outputs entirely within local or private infrastructure.
- Independent researchers can run security tests to find vulnerabilities.
- Organizations can apply their own access controls, logging, and compliance measures.
At the same time, being open-source doesn’t mean there’s full transparency across the entire development pipeline. For many AI systems labeled as open source, the origin, composition, and preprocessing of the training corpus aren’t made public, even when the model code is. This restricts independent verification of the model's training data, and may influence evaluations concerning privacy, bias, and trust.
DeepSeek doesn’t publicly disclose complete training datasets, which is consistent with this broader limitation and means that transparency at the code level doesn’t automatically extend to training data or development processes.
Centralized infrastructure and trust in ChatGPT
ChatGPT runs on infrastructure controlled by OpenAI. Users interact with the model through web or API interfaces, and all prompt processing occurs within OpenAI-managed systems.
In this model:
- OpenAI controls where and how data is processed.
- Users rely on documented policies rather than direct inspection of the code.
- Security controls, access restrictions, and monitoring are enforced centrally.
Because the underlying model and infrastructure are proprietary, external parties can't independently audit the full system. This limits transparency, but it allows OpenAI to standardize security controls and apply them consistently across all users.
Note that OpenAI has undergone controlled assessments and compliance reviews, including internal audits and third-party evaluations tied to security and regulatory requirements.
Technical safeguards: Encryption and access control
Both ChatGPT and DeepSeek employ a combination of encryption and access controls to protect user data within their platforms. These safeguards are designed to reduce the risk of unauthorized third-party access rather than to provide end-to-end confidentiality from the service provider itself.
Encryption in transit and at rest
Both platforms apply encryption to protect user data during transmission and while it’s stored on their systems.
ChatGPT encrypts data at rest using industry-standard encryption, such as 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). All endpoints use Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher to encrypt data that is sent between users, OpenAI, and OpenAI's service providers, which helps protect information from interception while it’s in transit over the network. The physical security of its infrastructure is managed by Microsoft Azure.
DeepSeek encrypts communication between users and its web servers using HTTPS (TLS), ensuring data in transit is protected from passive interception.
Access controls and account-level protections
Access controls determine who can access user data inside a platform and under what conditions. DeepSeek’s official documentation states that server and database access is restricted to authorized personnel through authentication and access control measures.
OpenAI implements strict access control measures based on the principles of least privilege and separation of duties. Access is granted only where necessary for operational, security, or legal purposes and is subject to regular review.
OpenAI also states that it continuously monitors and logs access activity. Logs are centrally collected and reviewed to detect unusual activity, and access permissions are periodically audited and revoked when no longer required. Administrative and internal systems require multi-factor authentication (MFA), and internal access changes are documented and reviewed.
Limitations of encryption in AI chatbots
AI chatbots don’t use end-to-end encryption (E2EE); to generate responses, services like ChatGPT and DeepSeek need to decrypt and process your prompts on their own servers.
This means that anything you enter can be used internally according to the platform’s rules (for example, for service operation, safety checks, quality review, or model improvement, depending on your settings). In other words, while encryption protects your data in transit and at rest, it doesn’t prevent the provider itself from accessing it.
Overall, encryption and access controls should be seen as important security protections, not as guarantees of complete privacy. It’s best to assume that anything you share with an AI chatbot may be stored or reviewed under the provider’s policies.
Business use and hosting scenarios
Businesses that integrate AI into their workflows or provide it with access to proprietary information through APIs need to account for data isolation, access control, compliance, and operational responsibility. These considerations vary depending on whether an AI tool is delivered as a hosted service or deployed within internal infrastructure.
ChatGPT Enterprise: Privacy, governance, and isolation controls
ChatGPT Enterprise is designed for organizations that want to use a hosted AI service while applying stronger governance and privacy controls than those available with consumer accounts.
OpenAI doesn’t use content submitted through ChatGPT Enterprise to train its models. Conversations are isolated at the organizational level, and access is governed through administrative controls rather than individual user settings. This allows organizations to manage how AI is used internally without relying on employees to configure privacy options on their own.
From a governance perspective, organizations can control user access, manage usage policies, and monitor activity across teams. This supports internal compliance requirements and audit processes. OpenAI still centrally manages the infrastructure, but these controls provide businesses with more defined boundaries for handling data within the service. This is particularly important when ChatGPT is used as an AI tool for developers or as a business intelligence AI tool, where prompts may include proprietary code, internal APIs, system designs, or sensitive analytical data.
ChatGPT Enterprise doesn’t change the hosted deployment model. Data is still processed on OpenAI-managed infrastructure, and organizations continue to rely on OpenAI’s security practices and internal access controls. The difference lies in how data is governed and isolated at the organizational level, rather than in where or how the infrastructure is operated.
Self-hosting DeepSeek: Benefits and responsibilities
DeepSeek can be self-hosted on an organization's internal infrastructure, such as on-premises servers or private cloud environments. This can allow for lower latency in some environments, and it offers more control over privacy and data retention and a customized setup. Prompts and outputs don’t leave the organization’s network, simplifying data governance and reducing exposure to third-party infrastructure.
For organizations in regulated fields like finance, healthcare, or government, self-hosting lets them use their current security measures, audit processes, and data storage rules directly with the AI system. Access can be restricted through internal identity systems, and usage can be monitored using the same logging and oversight tools already in place for other sensitive workloads.
However, self-hosting shifts responsibility to the organization. The business becomes responsible for securing the environment, managing access controls, monitoring usage, handling updates, and ensuring compliance with applicable laws and internal policies. It can also require many computational resources to run and fine-tune the model, and unlike API-based models, which are managed by the provider, you’ll need expertise to deploy and maintain the system.
In other words, the privacy and security outcomes depend on how well the organization designs and operates its environment, not on the default platform controls.
How to use AI tools more securely
ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and other AI chatbots are data-processing systems. Anything you input, whether by typing or voice, is stored and logged, and can be reviewed and retained for operational purposes. The same applies to uploaded files. That creates real exposure risks, especially when prompts include personal details, proprietary business information, or context that could be misused if accessed later.
Sensitive prompts can lead to corporate data leakage, compliance issues, or accidental disclosure of internal processes.
AI tools can also be exploited for social engineering, where attackers use AI-generated context to craft more convincing phishing or impersonation attempts.
Using AI securely means understanding where the boundaries are and adjusting how you interact with these tools accordingly.
Best practices to avoid sharing sensitive information
Don’t think of ChatGPT or DeepSeek as a friend or a confidante. If you have information that you wouldn’t tell a stranger, you shouldn’t share it with an AI chatbot.
- Avoid sharing direct identifiers and credentials: Never enter passwords, authentication codes, credit card numbers, bank details, or government-issued identification numbers.
- Be cautious with personal and location data: Full names combined with addresses, phone numbers, or email details can expose more than you intend, especially when prompts include personal context.
- Treat business information as sensitive by default: Internal documents, contracts, financial data, customer lists, and source code should not be shared in prompts unless the tool is explicitly approved for that use.
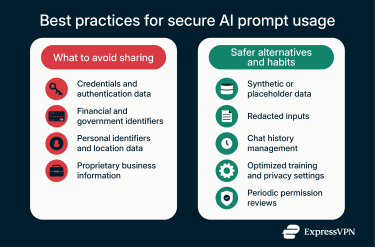
- Use synthetic or redacted inputs whenever possible: When you need help with a real scenario, replace real data with realistic placeholders. Synthetic examples allow you to get useful responses without exposing actual information. Redacting key details such as usernames, account numbers, or internal system names significantly reduces risk while keeping the prompt effective.
- Manage retention and training settings proactively: Many AI tools offer options to clear chat history or opt out of using prompts for model training. These settings are not always enabled by default. Reviewing and adjusting them helps limit long-term data retention and reduces the chance that sensitive prompts are reused internally.
- Review permissions and usage habits regularly: AI tools evolve quickly, and so do their settings. Periodically review privacy options, connected apps, and browser permissions to ensure that access remains aligned with how you intend to use the tool. Such oversight is especially important on shared devices or in team environments.
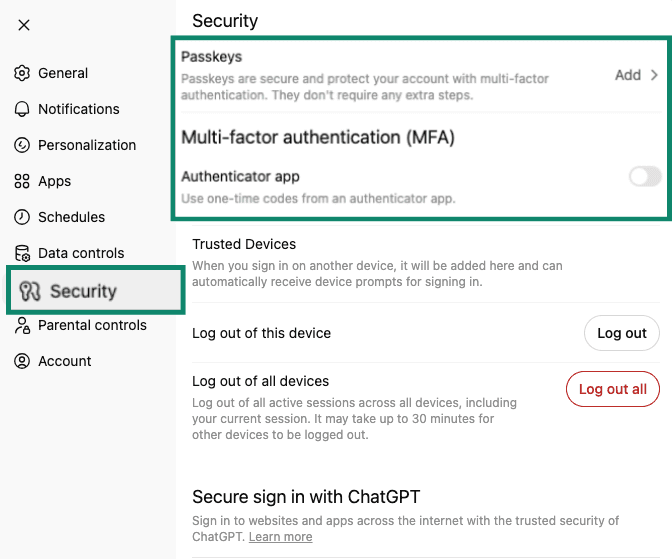
- Secure your account with a strong password: Your chat history and usage are tied to your account, so a compromised password could expose past conversations and potentially a substantial amount of sensitive data. Use a long, unique password to secure your account. If you use ChatGPT, enable MFA with an authenticator app or passkeys to prevent unauthorized access (at the time of writing, DeepSeek didn’t have these options). Note that MFA and passkeys are not available to all ChatGPT users: to check whether these features are available to you and to enable them, go to Settings > Security.
How a VPN can enhance privacy in AI usage
Using a virtual private network (VPN) with ChatGPT adds a layer of network-level protection to your sessions. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, which helps prevent third parties such as network operators or attackers on the same Wi-Fi network from intercepting your activity. It also replaces your IP address with that of the VPN server, reducing passive tracking at the connection level. This is especially useful when accessing AI tools on public or unsecured networks.
It’s important to understand the limits, though. When you log in to use the service, your activity is still associated with your account, regardless of whether you’re using a VPN or not. A VPN doesn't hide your prompts from the AI provider or stop the platform from processing or storing your input. What it does provide is protection against interception outside the AI service, which is especially useful when working remotely or traveling.
In enterprise environments, VPNs are often used alongside enterprise AI deployments or self-hosted models to provide layered protection. Unlike commercial VPNs, which are designed to anonymize consumer internet traffic, enterprise VPNs are generally part of the organization’s own network perimeter, enabling internal routing, identity-based access, and centralized policy enforcement. This setup reduces exposure by limiting where AI traffic flows and keeping sensitive prompts within controlled networks.
FAQ: Common questions about DeepSeek and ChatGPT
Does ChatGPT train on user conversations?
In the free, Plus, and Pro versions of ChatGPT, user conversations can be used to improve the models, depending on the account settings. Users can opt out of this use through their privacy controls. ChatGPT doesn't use conversations from business and enterprise accounts for model training.
Can either tool be used for confidential or regulated data?
ChatGPT Enterprise offers governance and data handling assurances for business use, while DeepSeek can be self-hosted, so data remains within internal systems. In regulated environments, organizations typically need clear policies, approved deployment models, and internal controls before using AI tools with sensitive data.
Is it safe to use a VPN with AI chatbots?
Using a VPN with AI chatbots is safe and doesn’t interfere with how the tools function. A VPN affects the network connection by encrypting traffic and masking your IP address, but it doesn’t change how the AI provider processes, stores, or accesses your prompts. It should be seen as a complementary privacy measure rather than a control over the chatbot itself.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN