Expressvpn Glossary
OpenSSH
What is OpenSSH?
Open Secure Shell (OpenSSH) is a free, open-source tool that lets users securely connect to remote computers and transfer data over a network. It encrypts communication between devices so that passwords and other sensitive information can’t be intercepted.
How does OpenSSH work?
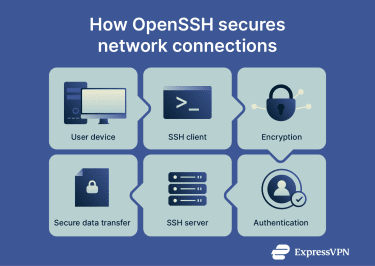 OpenSSH uses the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol to create an encrypted connection between two devices: the client, which is the user’s computer, and the server, which is the remote system the user is accessing.
OpenSSH uses the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol to create an encrypted connection between two devices: the client, which is the user’s computer, and the server, which is the remote system the user is accessing.
- Connection initiation: The OpenSSH client contacts the server. By default, this happens on port 22, though system administrators can change it, and often do, for security reasons.
- Key exchange and encryption setup: The client and server exchange cryptographic information to agree on secure encryption algorithms and generate a shared session key. This key, which is unique for each session, creates an encrypted tunnel and protects all data sent between them.
- User authentication: The user authenticates their identity to the server, within the encrypted tunnel, usually with a pair of public and private keys. This can also be done with a password, but key-based authentication is preferred over password authentication because it doesn’t transmit reusable credentials over the network that can be easier for cybercriminals to steal.
- Secure communication: Once authenticated, the two devices can communicate through a secure, encrypted link, which supports remote commands, file transfers, and secure tunneling through port forwarding. This ensures data, credentials, and commands remain private on networks.
Key features of OpenSSH
OpenSSH handles authentication, encryption, and data transfer within a single encrypted tunnel. The key features of OpenSSH include:
- Secure remote access: Uses encrypted SSH connections to safely manage remote systems over networks.
- Client and server tools: Comes with both a client (ssh) for connecting to other devices and a server daemon (sshd) that listens for and authenticates incoming connections.
- Encrypted file transfers: Provides Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) or SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for copying and transferring files securely between hosts.
- Key-based authentication: Supports public–private key pairs to verify identity without sending passwords, reducing the risk of brute-force attacks.
- Tunneling and port forwarding: Can encrypt data sent to servers or applications, such as web or database services, that don’t use SSH on their own.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Works across Linux, macOS, Windows, and other operating systems, allowing secure connections between different systems with minimal setup.
Why is OpenSSH important?
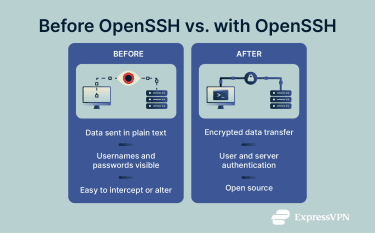 OpenSSH is the foundation of secure remote access and data transfer on the internet. Before OpenSSH, administrators relied on tools like Telnet and File Transfer Protocol (FTP), which sent data in plain text, making them easy targets for eavesdropping.
OpenSSH is the foundation of secure remote access and data transfer on the internet. Before OpenSSH, administrators relied on tools like Telnet and File Transfer Protocol (FTP), which sent data in plain text, making them easy targets for eavesdropping.
OpenSSH, on the other hand, encrypts all communication, which keeps sensitive data safe from interception, and it authenticates both users and servers to make sure connections are made only between trusted parties. Beyond security, OpenSSH is open-source and freely available for anyone to use or improve.
OpenSSH vs. SSH
SSH is the protocol that OpenSSH uses to enable secure communication between a user and a client. It was first developed in 1995 to replace older, unencrypted tools like Telnet. SSH-1 was then replaced by SSH-2, which introduced stronger encryption and authentication methods.
OpenSSH is a free, open-source implementation of the SSH-2 protocol. It was created by the OpenBSD project as an open-source alternative to proprietary SSH tools.
Both OpenSSH and proprietary SSH implementations offer the same functionality, including secure remote access, encrypted file transfers, and tunneling. OpenSSH is more commonly used because its open-source code is continually reviewed and updated by the security community, helping ensure transparency and reliability.
Common uses of OpenSSH
OpenSSH is used across networks and cloud environments to manage systems, transfer data securely, and automate administrative tasks. Common uses include:
- Remote server management: System administrators use OpenSSH to gain command-line access to servers and virtual machines for configuration, monitoring, and maintenance.
- File transfers: IT staff and developers use OpenSSH tools such as SCP and SFTP to move files between computers securely without exposing data to interception.
- Automated processes: Developers and operations teams use OpenSSH for machine-to-machine authentication in automated tasks such as backups, data synchronization, and software deployment.
- Network device administration: Network engineers use OpenSSH to manage routers, switches, and firewalls through secure command-line sessions.
- Tunneling and port forwarding: Administrators and security teams use OpenSSH to create secure channels for accessing internal services, such as databases or web applications, that are not directly exposed to the internet.
Further reading
- Post-quantum cryptography explained: What leaders need to know
- What is cybersecurity? Simple explanation + real-world examples
- SSL vs. TLS: Key differences and why TLS is better
FAQ
What does OpenSSH stand for?
OpenSSH stands for Open Secure Shell. It’s an open-source implementation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, designed to provide secure network communication through encryption and authentication.
Is OpenSSH the same as SSH?
Not exactly. Secure Shell (SSH) is the protocol that defines how secure communication between devices works. Open Secure Shell (OpenSSH) is a free, open-source implementation of that protocol, developed by the OpenBSD project. SSH refers to the underlying standard, while OpenSSH provides the actual tools that make it possible to use SSH for remote access and encrypted file transfers, such as ssh, sshd, scp, and sftp.
How does OpenSSH enhance security?
Open Secure Shell (OpenSSH) encrypts all data exchanged between devices, including passwords, commands, and files. It also verifies the identity of both systems before a connection is established, which prevents cybercriminals from intercepting or altering the data in transit.
What is the difference between OpenSSH client and server?
The Open Secure Shell (OpenSSH) client initiates a connection to another device, while the OpenSSH server identifies incoming requests and authenticates them. Together, they form the secure link that allows encrypted communication and data transfer between systems.
